ICT professionalism
FILTERS
THE 63 PROFESSIONAL PROFILES OF THE ICT SECTOR
IT
SAFETY
WEB
GIS
Synthetic description. Senior focal point for sales and customer satisfaction.
Mission. Build business relationships with customers to drive the sale of hardware, software, telecommunications or ICT services. Identifies opportunities and manages the acquisition and delivery of products to users. It is responsible for reaching sales targets and maintaining margins.
Synthetic description. Analyze the Information System to improve business performance.
Mission. Identifies areas where changes to the information system are required to support the business plan and monitors their impact in terms of change management. It contributes to the general functional requirements of the company with regard to the area of ICT solutions. Analyzes market needs and translates them into ICT solutions.
Synthetic description. It proposes plans and manages the functional and technical evolution of the Information System in the main business domain.
Mission. It manages and implements updates of existing applications and maintenance activities based on the needs, costs and plans agreed with internal users. It ensures the quality of service and the satisfaction of the internal customer.
Synthetic description. Develop and maintain Information Systems in accordance with the business and the needs of the organization.
Mission. Defines and implements ICT governance and strategy. Determines the resources needed for the implementation of the ICT strategy. Anticipates the evolution of the ICT market and the business needs of the company. Contributes to the development of the corporate strategic plan. Leads or participates in projects of greater change.
Synthetic description: Design, build, or monitor and maintain databases.
Mission: It ensures the design and implementation (Developer), or ensures the maintenance and repair of the company database (Administrator) to support information system solutions in line with the information needs of the business. Verify the development and design of database strategies, monitoring and improving database capacity and performance, and planning for future expansion needs. Plan, coordinate and implement security measures to safeguard the database.
Synthetic description: Build / code ICT solutions and write ICT product specifications in accordance with customer requirements
Mission: Ensures the creation and implementation of ICT applications. Contributes to planning and detailed design. Compiles diagnostic program and designs and writes code for operating systems and software to ensure maximum functionality and efficiency.
Synthetic description. Professional figure responsible for visual design and interaction between user and system throughout the life cycle of the system, from the definition and collection of requirements to the production of final design documents.
Mission. The UX Designer (or User Experience Designer) has the task of integrating user requirements, application requirements, accessibility and usability constraints into a visual interface and an interaction model (otherwise known as the "experience of the user ") as uniform and integrated as possible. The User Experience Designer is responsible for the development of a visual and interactive "style" that can at the same time characterize the Web application (providing it with distinctive characters) and guarantee effective achievement (bring it to the right point) and efficient (make it do the right number of clicks) of the user's goals.
Reference second generation profile. Digital Media Specialist.
Synthetic description: Designs and maintains the Enterprise Architecture
Mission: Find the balance between technological opportunities and business process requirements. It maintains a unified vision of the organization's strategy, processes, information and ICT assets. It relates the business mission, strategy and processes to the IT strategy.
Synthetic description: Promote understanding of how new ICT technologies add value to business.
Mission: It guarantees technological control to inform stakeholders about emerging technologies. It foresees and brings to maturity ICT projects through the introduction of appropriate technology. Communicate the value of new technologies for business. Contributes to the definition of the project.
Synthetic description: Manages assets, people and overall resources for ICT operations
Mission: Implements and maintains a part of the ICT infrastructure. Ensures that activities are conducted in accordance with company rules, processes and standards. It provides for the necessary changes according to the organization's strategy and cost control. Evaluates and suggests investments based on new technologies. Ensures the effectiveness of ICT and the management of associated risks.
Synthetic description: Manages the security policy of the Information System.
Mission: Defines the security policy of the Information System. Manages the spread of security through all information systems. Ensures the use of available information. Recognized as the ICT security policy expert by internal and external stakeholders.
Synthetic description: Ensures the implementation of the corporate security policy.
Mission: Proposes and implements the necessary security updates. Advises, supports, informs and provides safety training and awareness. It conducts direct actions on all or part of a network or system. He is recognized as the technical expert of ICT security by his colleagues.
Synthetic description: It educates and trains ICT professionals to achieve predefined standards of technical or business competence in ICT.
Mission: It provides the knowledge and skills necessary to ensure that learners are effectively capable of carrying out their tasks in the workplace.
Synthetic description. Ensures the alignment of the network, including telecommunications and / or computer infrastructures, to meet the company's communication needs.
Mission. It manages and operates on the networked information system, solving problems and errors to ensure defined service levels. Monitor and improve network performance.
Synthetic description. Manages projects to achieve optimal performance conforming to original specifications.
Mission. Defines, implements and manages projects from initial conception to final delivery. Responsible for obtaining optimal results, compliant with quality, safety and sustainability standards as well as consistent with the objectives, performance, costs and times defined.
Synthetic description: It ensures that the Information Systems are produced according to company policies (quality, risks, SLAs).
Mission: It acts and puts in place an ICT quality approach in accordance with the corporate culture. It ensures that management controls are properly implemented to safeguard assets, data integrity and operations. It is focused and committed to achieving quality goals and monitors statistics to predict quality outcomes.
Synthetic description: Provides the first line of telephone or email support for internal or external customers for technical aspects.
Mission: Provide user support and eliminate errors due to problems or critical aspects of ICT. The main objective is to allow the user to maximize productivity through the efficient use of ICT equipment or software applications.
Synthetic description: Plan, implement and manage solution delivery.
Mission: Manages the definition of Service Level Agreements (SLA), Operational Level Agreements (OLA) and Key Performance Indicators (KPI). Negotiate contracts in various business contexts or with customers and in agreement with the Business IS Manager. Manages staff that monitors, records and meets SLAs. Try to mitigate the effects if the SLAs are not met. Contributes to the development of the maintenance budget taking into account business / finance organizations.
Synthetic description: Administer ICT system components to meet service requirements.
Mission: Install software, configure and update ICT systems. It administers the operation of the system on a daily basis in order to satisfy the continuity of the service, rescues, safety and performance needs.
Synthetic description: Analyze requirements and specify software and systems.
Mission: It ensures the technical drawing and contributes to the implementation of new software and / or improvements.
Synthetic description: Plans and ensures the implementation and integration of software and / or ICT systems.
Mission: It designs, integrates and implements complex ICT solutions from a technical point of view. It ensures that the technical solutions, procedures and development models are up-to-date and compliant with standards. It is aware of technological developments and integrates them into new solutions. Acts as a team leader for developers and technical experts.
Synthetic description: Maintains and repairs hardware and software as requested by the customer.
Mission: Effectively maintains hardware / software. Responsible for timely and effective repairs in order to ensure optimal system performance and high customer satisfaction.
Synthetic description: Design and implement test plans.
Mission: It contributes to the correctness and completeness of a system by ensuring that the solution meets the technical and user requirements. It contributes in different areas of system development, testing system functionality, identifying anomalies and diagnosing their possible causes.
Brief definition: Top-level manager within the existing information security management system (if this is extended to the entire organization it may coincide with the CISO) as referred to by UNI CEI ISO / IEC 27001: 2014.
Mission: The information security management systems manager is the person delegated by the company management to coordinate the definition, implementation, maintenance and continuous improvement of the ISMS, in accordance with the requirements of the company security policy and current regulations. .
Reference second generation profile: ICT Security Manager.
Brief definition: Reference figure for the management of the safety of systems for the substitutive conservation of documentation in accordance with the law as referred to by CNIPA Resolution no. 11/2004, by the Ministerial Decree of 23.01.2004 and finally by the DPCM 03.12.2013. The profile is explicitly indicated in the accreditation document of public and private entities that carry out conservation activities of IT documents.
Mission: The security manager of the digital preservation systems defines and implements the security policies of the digital preservation system and governs its management, on the mandate of the Preservation Service Manager, working in concert with the person responsible for the processing of personal data, with the information security manager and, limited to PAs, with the information systems manager and the document management manager.
Reference second generation profile: ICT Security Manager.
Brief definition: Top-level manager for the management of ICT business continuity, as recalled by the guidelines for disaster recovery in the Public Administration pursuant to c. 3, letter b) of art. 50bis of the Digital Administration Code.
Mission: The role of the business continuity manager is to oversee the preparation of all the necessary measures to reduce the impact of an ICT emergency and to react promptly and effectively in the event of an interruption of the ICT functions, in support of the services provided. due to a disaster. It is also responsible for developing and maintaining the ICT business continuity plan and related documentation updated by planning and coordinating the execution of business continuity tests.
Reference second generation profile: ICT Security Manager.
Brief definition: The Chief information security officer, abbreviated to CISO, is, where present, the highest level manager of information security within the organization.
Mission: The CISO defines the strategy for the management of information security, coordinating the security managers, suppliers or specialist staff to ensure its continuous and correct implementation over time within a defined budget. To this end, given the transversal nature of information security, it also interfaces with the top management of the company and, according to competence, with all corporate responsibility figures.
Reference second generation profile: ICT Security Manager.
Brief definition: Reference figure for defined sets of activities and projects related to information security management, reports to the CISO (e.g. SOC Manager).
Mission: The information security manager oversees the implementation of the strategy defined by the CISO within his area of responsibility (be it a project, a process or a location), actively coordinating any operational figures assigned to him for this purpose, representing the natural link between the CISO and the rest of the staff with assigned tasks relating to information security.
Reference second generation profile: ICT Security Manager.
Brief definition: Position dedicated to the control of compliance with the defined rules and of the mandatory information security.
Mission: The process analyst is called upon to manage the periodic review of the processes relating to information security, highlighting any deviations detected with respect to internal rules, external regulations and international best practices on the subject according to the objectives set by the Management. It also interfaces with specialists to validate the actions necessary to remedy any deviations.
Reference second generation profile: ICT Security Specialist.
Synthetic definition. Operational figure dedicated to the technical verification of the information security of systems, networks and applications.
Mission. The technical analyst is called upon to manage the periodic examination of the security of systems, networks and applications, highlighting the technical vulnerabilities as well as any deviations detected with respect to internal rules, external regulations and international best practices on the subject according to the objectives set by the Management. It also interfaces with specialists to validate the actions necessary to remedy any deviations.
Reference second generation profile. ICT Security Specialist.
Synthetic definition. Operational figure dedicated to the technical analysis of the information security of systems, networks and applications in order to reconstruct their use over time.
Mission. The forensic analyst for ICT incidents is called upon to manage the collection of evidence and its analysis in conjunction with an information security incident, documenting everything so that it is correctly presentable in court.
Reference second generation profile. ICT Security Specialist.
Synthetic definition. Operational figure dedicated to the planning and implementation of processes related to information security management.
Mission. The process specialist manages the processes related to information security management day by day. It constantly interfaces with the other actors involved in the verification or organization of processes and contributes to their documentation.
Reference second generation profile. ICT Security Specialist.
Synthetic definition. Operational figure dedicated to the planning and implementation of information security solutions regarding systems and networks.
Mission. The infrastructure specialist manages the security of networks, systems and software responsible for network services on a day-to-day basis. They implement security controls as defined by the organization's policies, guidelines and standards. It constantly interfaces with the staff responsible for checking or organizing the infrastructures to contribute to their safety. It also deals with the technical documentation relating to infrastructural security.
Reference second generation profile. ICT Security Specialist.
Synthetic definition. Operational figure dedicated to the planning and implementation of security application solutions as well as aspects of secure programming.
Mission. The infrastructure specialist manages application security day by day by implementing security controls as defined by the organization's policies, guidelines and standards. It constantly interfaces with the personnel involved in the verification or development of the applications to contribute to their safety. It also deals with the technical documentation relating to application security.
Reference second generation profile. ICT Security Specialist.
Brief definition: Operational figure in charge of managing the response actions to information security incidents, member of a CERT or CSIRT.
Mission:. The expert in incident response is in charge of identifying and reporting possible indicators relating to information security. He also evaluates the events by correlating them with other data and proposes suggestions within the escalation process and then implements the defined response, reviewing and improving the process.
Reference second generation profile: ICT Security Specialist.
Synthetic description. Professional position in the Marketing sector & Digital communication that deals with managing virtual communities on the Web.
Mission. The Web Community Manager creates and helps to enhance relationships between the members of a virtual community on the Web and between it and the client organization, with effective communication within the group; in particular, it promotes, controls, analyzes and evaluates the conversations that take place on the various Web resources (websites, blogs, social networks). Builds and manages the relationship with online stakeholders. He can work as a freelance, for specialized Web marketing agencies or within an organization. In the latter case, in the Anglo-Saxon language, the term Internal Community Manager is also often used. He is also known as the Community Manager.
Reference second generation profile. Digital Media Specialist.
Synthetic description. Professional figure who deals with the management of activities related to a project in the Web environment. He is the project manager and must guarantee the realization of the project objectives by maximizing operational results, in compliance with economic constraints and to achieve customer satisfaction.
Mission. The Web Project Manager is a Project Manager specialized in the Web field who manages the project effectively, with the aim of achieving the project objectives agreed with the client, in compliance with time and costs. He is responsible for the project and it is he who defines, plans and coordinates the activities. Constantly monitors times, costs, quality, scope, risks and the achievement of expected results. In some cases he also holds the role of Team Manager of the project group; in this case he must motivate the team, coordinating it and delegating the various tasks. The Web Project Manager can be either an employee of the client, an employee of an external company in charge of managing the project, or a freelancer with a third party role.
Reference second generation profile. Project Manager.
Synthetic description. Professional position responsible for the management of prospect (potential) and / or loyal customers of a Web-oriented organization, also taking care of their customer satisfaction.
Mission. The Web Account Manager is part of the Web Marketing sector & Accounting. With the increased competition between organizations and greater attention to the quality of sales, the Web Account Manager has the delicate, as well as fundamental, task of acknowledging the needs and requirements of customers - potential and / or existing, transforming them into objectives that the organization arises. In particular, he manages negotiations and business relationships to facilitate the sale of products and / or services on the Internet and is responsible for reaching sales targets and maintaining margins.
Reference second generation profile. Account Manager.
Synthetic description: Create websites and multimedia applications by combining the power of digital technology with the effective use of graphics, audio, photographic images and videos.
Mission: Design, set up and code multimedia applications and websites to optimize the presentation of information, including marketing messages. It makes recommendations on technical interfaces and ensures sustainability through the application of appropriate content management systems.
Synthetic description. Professional figure who analyzes the client's business needs to allow the development team to produce adequate Web solutions.
Mission. The Web Business Analyst has the task of analyzing and defining business process flows, drafting the document with the results of the analysis and the collection of requirements. He is an expert in the subject / domain in which the Web product must be developed, must guarantee the integrity of the solution and alignment with business needs, or must be able to evaluate its economic and organizational impacts in order to allow the customer to draw the appropriate conclusions in terms of the sustainability of the solution.
Reference second generation profile. Business Analyst.
Synthetic description: Professional figure who has the task of creating and maintaining the databases used or managed by the organization in the context of activities related to the Web, managing the processes and documenting in a precise and exhaustive way what is in his area of competence.
Mission: The Web DB Administrator defines, designs and optimizes the structure of the databases. It guarantees the security of the database by taking care of the implementation of adequate data backup and recovery policies, ensures the high reliability of the databases and implements monitoring strategies, improves the performance of the databases using tuning techniques.
Reference second generation profile: Database Administrator.
Synthetic description: Professional position who, managing and supporting the development of Web services and digital marketing, is responsible for achieving the best return on investment (ROI) given by visibility within search engines and related services.
Mission: The Search Engine Expert takes care in the various phases of the project of the support and verification of the results concerning the positioning on search engines, imparting the rules of relative optimization within the development of Web services. Since the achievement and evaluation of the results are strongly linked to both the project and the type of intervention, he can work within an organization or, alternatively, as a freelance and for agencies specialized in Web marketing.
Reference second generation profile: Digital Media Specialist.
Synthetic description: Professional figure who deals with the planning and coordination of the entire promotion process, from the conception and preparation of advertising campaigns on the Web, up to the sale of products and / or services related to advertising, evaluating the costs and benefits of promotional action.
Mission: The Web Advertising Manager stimulates, using the Web, sales to customers: former customers, existing customers or new customers. The Web Advertising Manager defines the nature of the promotional campaigns in relation to the most appropriate Web communication media, in order to obtain the widest dissemination of the information being promoted. To obtain the greatest possible benefit, the Web Advertising Manager primarily identifies the "target" of the promotional campaign on the Web in relation to the type and quantity of recipients of such information. After activating the Web campaign, it evaluates the benefits, in relation to costs and so-called "leads" (eg new purchases of goods, activation of services, etc.).
Reference second generation profile: Digital Media Specialist.
Synthetic description: Professional figure who creates and / or codes Web based interfaces in accordance with the customer's requirements.
Mission: The Frontend Web Developer ensures the creation and implementation of Web based interfaces following the customer's specifications and referring to the user target. It contributes to the planning and definition of the output generated on the server side in collaboration with the Server Side Web Developer and / or the Web DB Administrator. Implement interface security in accordance with the Web Security Expert.
Reference second generation profile: Digital Media Specialist.
Synthetic description: Professional figure who deals with the creation of server-side Web applications, necessary for the generation of content for the Web and for the management of user interactions (transactions).
Mission: The Server Side Web Developer creates and / or contributes to the creation of Web applications using development languages for the Web; in particular, it creates, optimizes, verifies the functionality of the applications as well as the Web content generated by them by testing the public and confidential interfaces produced and / or integrated. Implement security in accordance with the Web Security Expert.
Reference second generation profile: Developer.
Synthetic description: Professional figure that is placed between the digital communication sector and marketing. Manage the contents of a website.
Mission: The Web Content Specialist is responsible for producing both textual and multimedia contents for which he is directly responsible, which are effective for a Web resource. He also takes care of the content based on the platform that will host it (website, social network, blog, interface ) and the target (user). You monitor the usability of the site with customer satisfaction tools. It can be freelance or part of an organization, public or private.
Reference second generation profile: Digital Media Specialist.
Synthetic description. Professional figure who administers the components of the ICT system to meet the requirements of the Web service.
Mission. The Web Server Administrator installs software, configures and updates ICT systems to ensure the operation of Web services. It administers the operation of the system on a daily basis in order to meet service continuity, backups, security and performance needs.
Reference second generation profile. Systems Administrator.
Synthetic description. Professional figure who mainly deals with identifying and representing the structure of the information and functional elements of a domain, in the context of a Web project, in order to facilitate their availability, functionality and usability, adopting a design approach centered on the 'user.
Mission. The Information Architect identifies and represents the structure of the information and functional elements of a domain, in the context of a Web project, through different channels of use, in order to favor their availability, functionality and usability, adopting an approach of user-centered design, and applying co-design methodologies (involving stakeholders and domain experts) and participatory design (involving a sample of end users).
Reference second generation profile. Systems Architect.
Synthetic description. Professional figure who supports the management of an organization in making strategic decisions relating to the presence and activities on the Internet and on the Web.
Mission. The Digital Strategic Planner understands the real needs and real needs related to the presence and activities on the Internet and on the Web of an organization. It supports the strategic choices indicated by top management and provides operational inputs to the other professional figures involved in the process.
Reference second generation profile. Service Manager.
Synthetic description. Professional figure who analyzes the reference IT context, evaluates and proposes the appropriate security policy in accordance with company policies and the specific context. You are responsible for periodically checking the security of the system and carrying out the appropriate tests (eg. Penetration Test). It also takes care of the aspects of training and awareness on safety issues.
Mission. The Web Security Expert analyzes the reference context, evaluates and proposes the appropriate security policy to be implemented in accordance with company policies to protect applications, Web servers, data and related processes. It analyzes the scenarios of possible attacks and defines the technical security requirements. It is responsible for the security checks during the various phases of the realization of a web project and / or for the periodic checks after release. You can personally take care of implementing Security strategies by performing direct actions on various objects that need protection such as architectures, networks, systems or applications.
Reference second generation profile. ICT Security Specialist.
Synthetic description. Professional figure who creates / codes application solutions for mobile peripherals and writes application specifications for mobile peripherals in accordance with customer requirements.
Mission. The Mobile Application Developer ensures the creation and implementation of applications for mobile devices that can also interact with the Internet and the Web. It contributes to the planning and definition of application details. It carries out simulations to verify the operation of the application to ensure maximum functionality and efficiency.
Reference second generation profile. Developer.
Synthetic description. Professional position responsible for the "income statement of the online store on the Web", the assortment, merchandising activities and in-store promotions.
Mission. The Online Store Manager helps to generate value for the company to achieve its objectives through e-commerce in line with the positioning that it has decided to give itself in terms of the relationship between digital and physical channels.
Reference second generation profile. ICT Operations Manager.
Synthetic description. Professional figure responsible for the design and implementation of augmented reality systems in particular for internet and Web Based environments. You are responsible for designing and implementing augmented reality experiences for the Web starting from the visual design of the interface up to the interaction between user and system, throughout the life cycle of the system.
Mission. The Web Augmented Reality Expert has the task of designing and implementing effective augmented reality experiences, in particular for internet and Web Based environments. Apply the principles of accessibility and usability of interfaces and create positive and consistent interaction models, based on user analysis and the type of experience you want to create. He has interdisciplinary knowledge, analyzes and selects technologies useful for the design of augmented reality. During the augmented reality design process, it focuses on the expected results and is able to conduct, once the prototype of the experience is finished, an evaluation of the same by monitoring the experiments with small groups of users.
Reference second generation profile. Developer.
Synthetic description. Professional position that deals with analyzing, managing and influencing the reputation of anyone (organization or individual) present on the Internet and on the Web.
Mission. The Reputation Manager helps to create the best context for the achievement of corporate or personal objectives by intervening on all occasions in which online conversations can be detrimental to the image of the company and its products. Promotes and disseminates brand awareness through an appropriate digital PR activity.
Reference second generation profile. Digital Media Specialist.
Synthetic description. Professional figure who promotes activities related to the management and communication of corporate knowledge, identifying methods, tools, processes and practices aimed at encouraging the development of intellectual capital through sharing.
Mission. The Knowledge Manager oversees the knowledge-related activities (database, historical archives, data catalogs) of the company. It exposes the processes of management and emergence of knowledge through internal and external sharing, to disseminate it on participatory platforms, in particular those residing on the Web (eg wiki, datahub, social coding), preserving the specificities subject to patents.
Reference second generation profile. Service Manager.
Synthetic description. Professional figure expert in online teaching processes and methodologies. Coordinates and develops training courses in distance, blended, rapid, mobile and ubiquitous learning modes.
Mission. The E-Learning Specialist has the task of designing, managing and monitoring online learning paths and environments, choosing and applying technologies, approaches and didactic strategies for the different levels and contexts of formal and non-formal learning, taking into account the rapid and continuous evolution of models of construction and dissemination of knowledge and learning on the Web.
Reference second generation profile. ICT Trainer.
Synthetic description. Professional position responsible for the activities, generally carried out in internet and Web based environments, of collection, analysis, processing, interpretation, dissemination and display of quantitative or quantifiable data of the organization for analytical, predictive or strategic purposes.
Mission. Il Web Data Scientist identifica, raccoglie, prepara, valida, analizza, interpreta dati inerenti a diverse attività dell’organizzazione per estrarne informazione (di sintesi o derivata dall’analisi), anche tramite lo sviluppo di modelli predittivi per generare sistemi organizzati di conoscenza avanzati. Grazie alla conoscenza approfondita del business e/o missione dell’organizzazione individua e accede alle fonti di dati in grado di sostenere e sviluppare un determinato processo aziendale; sceglie metodi e modelli più idonei ed efficaci per guidare le scelte strategiche aziendali, sviluppare linee di evoluzione e piani operativi; astrae le informazioni reperite e, tramite queste, genera indicazioni e programmi di sviluppo dell’azione. Presenta queste indicazioni nella forma più idonea a supportare le decisioni tattiche e strategiche del management, prestando particolare attenzione alle problematiche connesse alla sintesi e alla rappresentazione e visualizzazione efficace delle informazioni.
Reference second generation profile. Digital Media Specialist.
Synthetic description. The Wikipedian collaborates on Wikimedia projects (wikimedia.org) including Wikipedia, also creating and modifying entries and contents.
Mission. The Wikipedian, framed within an institution (both public and private) or a company, is defined "Wikipedian in Residence" and acts as a link between the "residence" structure and the Wikipedia community (and / or other projects, such as Wikimedia Commons, Wikisource or Wikidata), to promote mutually beneficial cooperation. Within the structure in which it operates, it identifies and enhances the data and materials useful for the growth of the Wikimedian community, making them available, verifying the neutral point of view, through open licenses and encouraging dialogue between people for the improvement of contents in order to to increase the reputation of the residence facility.
Reference second generation profile. Digital Media Specialist.
Synthetic description. Figura professionale esperta dei processi, delle metodologie e delle tecnologie di acquisizione e di manipolazione di dati geospaziali. Si occupa di analizzare i dati di natura spaziale per fornire al management le informazioni utili a disegnare strategie e prendere decisioni, nonché per produrre informazione e nuova conoscenza atta a concretizzare attività di problem solving. Particolare attenzione è rivolta al contesto dei «Big Data» di tipo spaziale, dove il GDA deve orientarsi tra grandi volumi di dati allo scopo di individuare, sintetizzare e mostrare il dato utile ad affrontare un problema o a semplificare una decisione complessa. Il GDA garantisce la provenienza, la funzionalità e l’usabilità del dato geo-spaziale.
Mission. The GDA interacts with geo-spatial data in the context of activities relating to the origin, the management of meta-documentation, the manipulation / transformation and analysis of the same. Therefore, this professional figure has a strong ability to understand the origin, the acquisition methods and technologies, and the formats and quality of geo-spatial data, as well as the manipulation processes within the production flows of the data themselves. Furthermore, this professional figure must be able to publish the results of their analyzes according to the most common methods of spreading geo-spatial data. Therefore, it must determine or define the most appropriate structures for such data and its components, as well as know how to use web-oriented applications for online publication of data and the creation of maps for specific uses.
Reference second generation profile. Systems Analyst.
Synthetic description. Professional figure included in the governance bodies of an organization, to support and govern the conscious use of geographic data and technologies available for their collection, management and sharing, with particular attention also to the development of IDTs. The actions of the GIM facilitate the increase of digital competence within the network that makes up an organization oriented to a conscious use of geographic data with regard to the problems related to the ability to use such data, understood both with respect to the availability of this information. , both as skills acquired for their exploitation.
Mission. Attributed to the geographical value of "raw material" for the creation of innovative products and services, the GIM identifies the existing supply chains within the organization, coordinates the collection and validation of geographic data relating to the activities and analyzes their contents both to extract useful information to generate value, and to produce knowledge to be given back to the territory. In particular, on the basis of the analysis of the production flows carried out within the organization, the GIM identifies the data characterized by a geographical dimension or which could potentially possess it, evaluates their use, purposes and "performance" in terms of actual use with respect to potential. Furthermore, thanks to the in-depth knowledge of the business and / or mission of the organization, this professional figure highlights the sequences of activities already in place or potentially feasible that can significantly contribute to the realization of valuable services as a set of processes or support systems. to decisions.
Reference second generation profile. Chief Information Officer (CIO).
Synthetic description. Professional position responsible for managing the activities, people and overall resources of the Geographic Information System (GIS) structure of an organization, as well as the wider context related to the construction of spatial data infrastructures (IDT).
Mission. It ensures that the activities of the GIS structure are conducted in accordance with the rules, processes and standards of the organization. It provides for the necessary changes according to the organization's strategy and cost control. Evaluates and suggests investments based on new technologies. Ensures the effectiveness of the GIS and the management of associated risks. It ensures that the interoperability and sharing of spatial data and services based on them follow specific standards and procedures of the GI.
Reference second generation profile. Project Manager.
Synthetic description. Professional figure expert in the most common processing of geographic information: acquisition, collection, creation, editing and processing of all types of data (raster, vector, database) in the context of GIS applications, possibly starting from various information sources, including non-spatial ones, including non-digital ones (eg paper documents and maps); creation of customized GIS maps and applications; presentation of numerical, graphical and cartographic results. It supports specialists in the various sectors (urban planners, analysts, geologists, etc.), public administrations or companies in the development, management, updating and use of geographic information systems even in the broader context of the construction of spatial data infrastructures (IDT) .
Mission. Coordinating with the organizational and technical managerial level, the GI Technician is responsible for carrying out a series of basic GIS operations for the development of databases, cartographic production and the design, implementation and management of geographic information systems.
Reference second generation profile. Database Administrator.
Synthetic description. Professional figure expert in spatial literacy and methodologies for the development of spatial thinking and geo-digital skills in the context of the network that makes up an organization oriented to an informed use of geographical data in regard to the problems related to the ability to use such data, understood both with respect to the availability of this information, and as skills acquired for their exploitation.
Mission. The fundamental task of the GKE concerns the promotion of spatial awareness through the development of spatial thinking within the network of the organization's actors. Detect the necessary geospatial skills. Plans training interventions for the development of these skills and for the formation of "spatial citizenship", allowing individuals and groups to interact and participate in social spatial decision-making processes, thanks to the correct production and use of geo-media (eg maps, virtual globes, GIS and Geoweb), guaranteeing the creation of stable and lasting services as well as the growth of spatially connected users. The GKE can support the GIM in the context of complex organizational ecosystems.
Reference second generation profile. ICT Trainer.
DEFINITIONS OF ROLES
The English terms used in the various profiles identify the role played by a user within the company or project on which he works.
Manager: the manager of an activity / department, with management and organization duties; Specialist: those who work in a specific area (halfway between a salesman and a technician); Developer: who carries out coding / programming tasks; Technician/Expert: who has technical / specialist responsibilities; Designer: who has design duties; Trainer: who has training duties; Analyst: who has analytical duties; Architect: who designs a complex structure; Administrator: who has administrative duties; Planner: who has planning duties
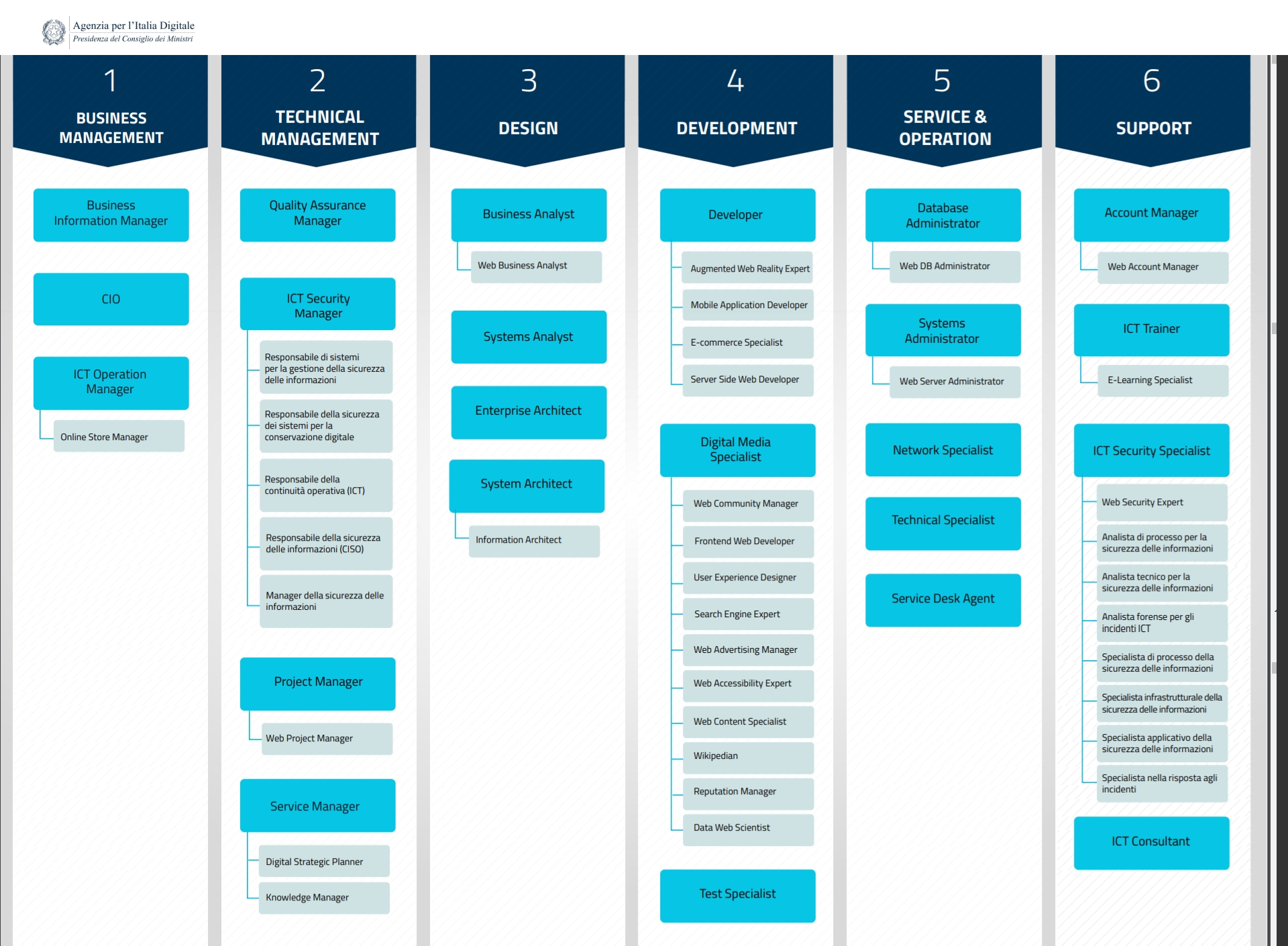
List of 63 ICT professional profiles recognized in Italy (AGID), divided by the 4 areas of belonging (IT, Sicurezza, Web e GIS) e filtrabili per tipo di attività o area di competenza.
ICT Skills and Professionalism
Negli ultimi 30 anni, il boom delle tecnologie digitali ha reso necessario lo sviluppo di competenze e professionalità specifiche legate al mondo ICT: in pochi anni, le figure legate al settore delle tecnologie digitali si sono moltiplicate per abbracciare i vari ambiti legati al settore ICT.
Capita spesso che quando un'azienda o un privato si trovano a dover realizzare un progetto in ambito digitale, sorga la necessità di capire quali competenze poter/dover sviluppare internamente e soprattutto a quali figure affidarsi per sviluppare i propri progetti in ambito digitale: data la grande varietà di fugure professionali presenti in ambito ICT non sempre è semplice e immediato distinguere le specificità e le competenze delle singole professionalità ICT e riconoscere le figure più adatte cui affidarsi.
Già dai primi anni 2000 l'UE è corsa in aiuto delle aziende europee iniziando ad organizzare il mondo delle tecnologie digitali attraverso il EUCIP program, individuando 21 professionalità ICT (riconosciute nel 2005 anche dal primo Italian ICT classification model) e, nel 2014, ha reso disponibile l'e-Competence framework, una guida di riferimento per i paesi dell'UE, che semplifica il riconoscimento delle competenze digitali e delle professionalità legate al settore digitale. Grazie al contributo proposto dall'EU, nel 2017 l'AGID (l'organo ministeriale italiano per lo sviluppo digitale), ha organizzato il settore digital italiano riconoscendo 63 professonalità ICT (tra progettisti, tecnici, consulenti, operatori e assistenti in ambito ICT) e specificandone le relative competenze.
Digital skills
Le competenze digitali (digital skills) are a universe of technological skills, ranging from basic ones such as the use of computers or basic software (e.g. Microsoft Word), to more specific and advanced ones such as software development or artificial intelligence.
In order to better understand the differences between the various digital skills and their degree of specificity, in the world of work it is customary to divide digital skills into 3 reference levels: basic, intermediate and advanced.
|
BASE BASIC DIGITAL SKILLS Basic level skills that people manage to acquire independently |
INTERMEDIATE INTERMEDIATE DIGITAL SKILLS Intermediate level skills that are learned through specific courses |
ADVANCED ADVANCED DIGITAL SKILLS Technical level skills that are developed with university and / or professional courses |
|
Examples
|
Examples
|
Examples
|
Fig 1: The 3 levels into which digital skills are divided (Source THAT)
Un'altra suddivisione delle competenze digitali è quella proposta nei curricula tra "digital Soft Skills" e "digital Hard Skills": le competenze digitali "leggere" identificano le capacità digitali di base più generiche (navigazione web, invio mail, scrittura testi ecc.), mentre le digital hard skills identify all those more structured and specific skills that concern the use of certain software or the competence to carry out specialized digital activities (eg programming, html design, CAD design, etc.). In particular, the list of digital hard skills in the curricula, facilitates the identification of a specific ICT professional figure and the identification of sector specialists.
ICT sector organization
Neli ultimi 20 anni, il grande sviluppo delle tecnologie digitali ICT, ha determinato la nascita di nuove professionalità legate al settore digital: alle attività tecniche più classiche dello sviluppo hardware/software (ad es. programmatori, sistemisti e tecnici hardware), si sono unite quelle legate al mondo della comunicazione digitale (ad es. designer, sviluppatori web, Tecnici ICT, tecnici delle telecomunicazioni, SEO, marketer, social manager, formatori digitali ecc.).
Nel 2014, per aiutare privati e aziende ad orientarsi al meglio in ambito digital e per aumentare la trasparenza, la mobilità e l’efficienza nella gestione risorse umane del settore ICT, l'Unione Europea ha reso disponibile uno schema di riferimento chiamato e-Competence Framework (e-CF) UNI EN 16234-1, che identifica ed organizza le professionalità legate al mondo digital e ne specifica le relative competenze.
L' e-Competence Framework rappresenta oggi il quadro di riferimento europeo per l'identificazione delle competenze ICT e serve a semplificare l'identificazione delle competenze digitali dei singoli professionisti e a rendere possibile l’identificazione di skills che possono essere richieste per svolgere correttamente un compito in ambito digitale. Nell' e-CF vengono individuate 40 competenze relative al settore ICT, suddivise in 5 gruppi principali:
- PLAN (PIANIFICARE)
- BUILD (REALIZZARE)
- RUN (OPERARE)
- ENABLE (ABILITARE)
- MANAGE (GESTIRE)
Fig 3: Schema di base Europeo delle competenze ICT (e-Competence framework) Vedi anche: Mapping and detailed explanation of skills
The identification of ICT professionals, their organization and the definition of their respective competences proposed by the e-CF, has a triple effect:
- the identification of a standardized, structured and shared ICT organization for the whole European Union, allows EU states to more easily organize their internal ICT sector and simplifies international mobility and collaboration in the ICT field;
- guides private and public companies in the search for the skills most congenial to them for the development of their digital projects or for the resolution of their problems in the ICT field;
- guides professionals in the ICT sector as regards the skills that each figure must develop in their own working environment and defines the operational boundaries between the various figures identified;
ICT professional profiles
In Italy, the adoption of the e-Competence Framework has resulted in the identification of over 60 professionals related to the ICT sector (see above List of ICT professionals), organized in 4 areas (IT, WEB, GIS, Security) and 6 areas of competence (Business management, Project management, Technical management, Design, Development, Support). Furthermore, of each ICT figure identified the area of competence is specified.
Le linee guida italiane per l'organizzazione del settore ICT, permettono ad aziende e privati italiani di orientarsi al meglio nell'individuazione delle figure più adatte per sviluppare i propri progetti digitali e permette ai professionisti dell'ambito digitale di avere un quadro completo delle competenze richieste nel proprio ambito professionale.
Fig 2: Schema italiano delle competenze ICT (Fonte AGID)
I 4 AMBITI ICT
THE 6 AREAS OF COMPETENCE
L'ambito di coloro che sviluppano e offrono assistenza sui progetti hardware e software, cui appartengono programmatori, progettisti hardware, tecnici IT, specialisti delle reti, responsabili della sicurezza IT ecc;
L’ambito legato ai tecnici che operano per la sicurezza dei sistemi operativi aziendali, dei software e delle strutture online (siti e cloud);
The dress linked to online communication, which includes designers, web developers, marketers, ecommerce specialists, data analysts, social managers and all those related to the development of web resources;
The area related to geographic / territorial information to which the Technicians related to the world of design and development of GIS information systems and digital cartography belong;
It includes those who have to manage a project from the point of view business and economic and they must know how to guarantee a ROI.
Includes those who must coordinate stakeholders involved in a digital project: it assumes the use of Project Management techniques applied to the ICT context.
Includes those who think of technical management structures that guarantee the correct functioning of the digital product created.
Includes managers of technical and architectural design: includes the collection of requirements and the definition of the functional needs that the project must meet.
Includes managers of technical construction of the project, then development, integration and testing.
Includes those who exercise user support activities necessary for the service to function: also include commercial relations between customers and suppliers.
To consult the complete list of the 63 ICT professionals recognized in Italy (AGID), see above List of ICT professionals.
Insights
- Guidelines for the quality of digital skills in ICT professionalism (AGID website - Agency for digital Italy)
- ICT professionalism (AGID website - Agency for digital Italy)
- Web Skill profiles
Birth and development of ICT
ICT is the sector linked to digital communication and includes all aspects relating to the development of hardware technologies, software, web and GIS: public and corporate networks, software, mobile apps, websites, eCommerce, cloud services etc. they are all ICT technologies widely spread and used all over the world.
In just over half a century, from the development of the first software and the first fixed PCs, reserved exclusively for business use, there has been a massive use of the web and digital technologies in both the public and private sectors.
From information technology to ICT
Negli ultimi 40 anni, lo sviluppo delle tecnologie digitali, ha subito 3 importanti fasi di trasformazione che hanno portato il settore dell'informatica degli anni '80 a trasformarsi nel settore delle tecnologie IT negli anni '90, fino a trasformarsi nel settore delle tecnologie ICT alla fine degli anni '90:
- Informatica (programmazione di software): negli anni '80 si è sviluppato nella società civile l’uso dei primi computer ed è nata l’informatica come attività tecnica di sviluppo di software e gestionali per le aziende che possedevano computer o altri device fissi (vedi storia computer dal 1980 al 1989);
- IT development (tecnologie hardware/software): negli anno '90 si è diffuso l’uso privato ed aziendale di PC, router, reti cablate, bancomat ecc. e si sono sviluppate le attività di progettazione e sviluppo delle componenti hardware e software dei vari device fissi (vedi storia computer dal 1990 al 1999);
- ICT development (tecnologie internet/mobile): il primo decennio degli anni 2000 è stato quello che ha visto il boom di internet e dei device mobili e sono nate tutte le attuali forme di comunicazione digitale: mobile device, reti wifi, gps, siti aziendali, social, eCommerce, analisi big-data, digital marketing, servizi cloud ecc. (vedi storia computer dal 2000 al 2010);
Negli ultimi 20 anni l’ICT ha trasformato sia il modo di comunicare delle persone, sia il modo di agire e relazionarsi delle persone tra di loro e con i servizi che le circondano, tanto da rappresentare una vera e propria rivoluzione (digital revolution) tutt’ora in corso: comunicare tramite mail, con messaggi whatsapp, pubblicare un post sui social, usare un motore di ricerca, fare un acquisto online, prenotare una vacanza online, documentarsi sul web, usare GPS e mappe digitali ecc. sono tutte attività comuni e spesso indispensabili.
Oggi, le persone passano in media circa 4,5 ore a day connected to the internet to meet their digital communication needs and much of the economy has now moved to the web thanks to the spread of online sales, home banking, paypal payments, logistics management, cloud services, online marketing, etc. all activities that today participate in developing thedigital economy.
Future of ICT
In the next few years, with the development of Web 4.0 and Industry 4.0, ICT is preparing to play an even more important and decisive role for the socio-economic development of societies: the use of automation, robots, augmented reality, artificial intelligence, internet of things and big data, will play a role increasingly prominent to connect people with each other and with the world around them.
Molti analisti socio-economici prevedono nel prossimo futuro, un peso sempre maggiore delle tecnologie digitali che, come è avvenuto per l'industrializzazione del '900, diventeranno sempre più influenti nel determnare lo sviluppo e la ricchezza dei popoli: nei prossimi anni le città diventeranno sempre più "smart city".